What is a dental filling?
A dental filling is a dental restorative material used to restore the function, integrity and morphology of missing tooth structure. Function, integrity and morphology are lost as a result of decay or trauma and this may also result in pain.
Dental fillings can be either direct restorative materials or indirect restorative materials and this depends on whether they can be placed directly in the prepared tooth cavity or if they are first prepared in the lab before they are placed in the cavity.
There are plenty of options when it comes to dental fillings which have been developed over time, each improvement designed to fill a deficiency. Each improvement also came along with a sacrifice for a strong quality of the older material. This leads to the various advantages and disadvantages of the various filling materials.
The decision on which material would be ideal for your unique case is made with your dentist while putting into consideration the different properties of each.
Types of Dental Fillings
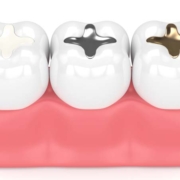
1. Amalgam dental fillings
This is an alloy containing silver, mercury in the larger proportions with other metals being present in small quantities. It has been present for over 150 years and has been designed and redesigned which qualifies its being the most widely used filling material.
Advantages
- It is cheaper than all the other filling materials
- It has low shrinkage and henceforth little to no leakage
- It is very durable
- It can withstand strong biting forces, can be placed in one visit and is resistant to further decay.
Disadvantages
- It is not aesthetically pleasant due to its contrast with the natural tooth colour
- It is not preservative since placing it requires destruction of healthy tooth structure, the residues if not well handled can pollute the environment. Despite the aggressive anti amalgam campaigns, there has not been any evidence supporting the theory that enough mercury leaks into the blood to cause any diseases.
2. Composite dental fillings
This is made up of an acrylic resin and powdered glass like particles. It is tooth coloured and can either harden on its own or can be cured using UV light.
Advantages
- Aesthetically pleasing since there are many shades to match the various natural tooth colour
- It can be placed in one visit
- It is durable, can be used for both front and back teeth, and can withstand moderate biting forces
- There is preservation of tooth structure, no corrosion and a low risk of breaking if it is well bonded above the enamel layer
Disadvantages
- It is costly
- It is not as strong as amalgam
- It is more difficult to place
- It may leak with time if bonded below the dentin surface.
3. Glass ionomer
This is made up of acrylic acid and fine glass powders. It is usually used on the root surface cavities and in areas without very strong biting forces. It is also used to cement crowns.
Advantages
- Aesthetically pleasing since it resembles tooth structure
- It can contain fluoride which gives prophylaxis against caries
- It preserves tooth structure during its placement, it can be completed in a single visit and allergic reactions are rare.
Disadvantages
- Limited application because it cannot withstand strong biting forces
- It is a bit costly
- It may become rough with age allowing plaque to build up and consequently caries development.
4. Resin Ionomer
It is made up of a glass filler, acrylic acids and acrylic resins. It is usually used for fillings on the non-chewing substances and for fillings on decidual (milk) teeth.
Advantages
- It is aesthetically pleasing, even more translucent than glass ionomer which brings it to resemble dentin more closely
- It can be placed in a single visit
- It does not require destruction of the healthy tooth structure
- It lasts longer than glass ionomer albeit not as long as composite does and the fluoride it contains is prophylactic against caries.
Disadvantages
- It has limited application,
- It is moderately costly and wears fast so it would require replacement.
5. Porcelain
It is used to make indirect restorations for example crowns, veneers, inlays and on lays. It can also be used n combination with a metal to make porcelain fused to metal crown.
Advantages
- Aesthetically pleasing, it has good resistance to further decay, resistant to surface wear.
- Due to its precise fitting, it also does not have leakage and thus no secondary caries develop.
- Allergic reactions to it are rare.
Disadvantages
- It is brittle and thus can easily break
- It is costly and needs a minimum of two visits.
6. Gold alloys
These contain gold, copper and other metals. Gold being the elite metal it is, forms a strong and efficient material for crowns, bridges, on lays and in lays.
Advantages
- No corrosion
- Has excellent durability
- Resistant to bite forces,
- Its placement preserves the healthy tooth structure and it resists leakage.
Disadvantages
- It is costly (obviously), it is not tooth colored and so in case one does not want the attention
- It is inconveniencing, and it needs more than a single appointment to be placed.
Are you having teeth cavities and are in need of a dental filling? Book an appointment with our dentist today and we will work out a customized affordable treatment plan for you.