Mouth Cancer: What you need to know
In the UK, this is a season of transition. The leaves fall from the trees in all shades, bringing color to sidewalks and parks and adding a euphoria to endings. In November, the UK also commemorates Mouth Cancer Awareness month and in solidarity, we are joining in to bring awareness to this malady that is often overlooked and yet it takes people in droves to painful miserable deaths. This month, we remember those who fought and lost and we celebrate those who fought and won and those who are fighting even now. And also, we bring it to the attention of those who are not aware of the existence of search a grueling battle against such a relentless foe; mouth cancer.
What is mouth cancer?
Mouth cancer is just like any other type of cancer, even occurring the same way except that it occurs in the mouth and the surrounding structures. It starts out as a failure of cells to regulate their proliferation when the innate genetic structure has oncogenes incorporated in them. This causes tissue destruction which can manifest as sores and can also result in swelling of the tissue which results in the tumor like growth of the tissues.
Forms of mouth cancer
Mouth cancer can develop on the lips, on the lining of the mouth (oral mucosa), the tongue, the salivary glands, the oropharynx and even the tonsillar tissues. The kinds of mouth cancer are named basing on the type of tissues that are affected. These are;
- Squamous cell carcinoma; this develops from squamous cells which are cells found in the lining of the mouth.
- Adenocarcinoma; this develops from glandular tissue.
- Lymphoma: this develops from lymphoid tissues e.g. the tonsils.
- Sarcoma; this develops from bone and cartilage tissue cells.
- Oral malignant melanoma: this develops in the cells that produce melanin, the melanocytes.
The tongue is the most commonly affected part, followed by the palate, buccal mucosa and the floor of the mouth. The percentages of the prevalence are 34.6%, 13.5%, 13.3%, 12.2%.
Causes of mouth cancer
The etiology of mouth cancer is such that even if you brushed your teeth diligently, you cannot safeguard yourself totally from it. There are other factors which play roles, ranging from subtle to magnanimous levels in their influence. These are;
- Alcohol; alcohol plays a role in the development of mouth cancer as a result of the carcinogens that it holds. Excessive consumption of alcohol is actually one of the top causes of mouth cancer.
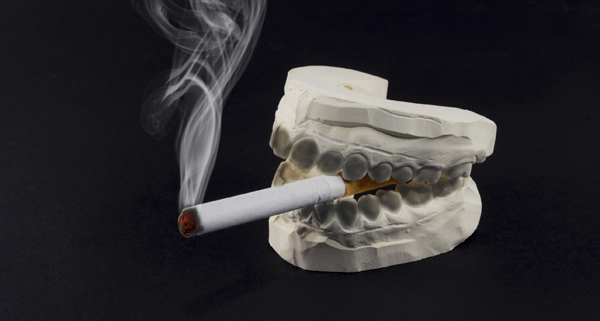
- Tobacco: tobacco, whether smoked or chewed still has the same disastrous effects on one’s health, often culminating in lung or mouth cancer. It contains numerous carcinogens and all these play a role in fueling the development of mouth cancer.
- HPV-16; the human papilloma virus is a sexually transmitted disease that has spread rapidly with the increasingly promiscuous culture of contemporary society. Type 16 of the virus can trigger oncogenesis especially in the immunocompromised people for example those living with AIDS, those on immunosuppressing drugs and so on.
- Sun exposure: this especially holds true for the lower lip, where it is exposed to the ultraviolet radiation from the sun which is a potent carcinogen.
- Family history; if one has a history of mouth cancer in their family, there are changes that they will get and henceforth they ought to be vigilant.
Symptoms of mouth cancer
The symptoms of mouth cancer are many and very variable and this means that not everyone will get the same presentation in case they get mouth cancer. These are symptoms everyone should pay attention to and seek an explanation for as early as possible so as to start treatment early which improves the prognosis for mouth cancer.
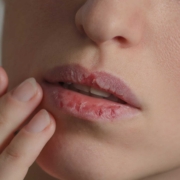
- White or red patches present in the mouth for longer than two weeks
- A painful sore that lasts longer than two weeks
- A sore throat coupled with a chocking sensation
- Unexplainable swellings in the mouth
- Ear pain
- Numbness
- Tooth loss
- Mobile teeth in the sockets
- Swelling of the jaws
The above are some of the things that may not be a confirmation for, but are signs of mouth cancer.
Diagnosis of mouth cancer
Mouth cancer can only be confirmed after diagnosis and this is done by taking a biopsy and studying its pathology after which presence or absence of cancer cells will be determined. Mouth cancer screening is usually offered at dental care facilities and considering the fact that it is not debilitating, it should be routinely considered especially in the high risk people.
Treatment for mouth cancer
Treatment for mouth cancer can involve surgery, where the cancerous structures are cut out. It may also include radiotherapy where high intensity radiations are used to kill the cancerous cells and also chemotherapy which involves usage of drugs to kill these cells. Mouth cancer can be treated and healed, however the rate of healing is highly dependent on the stage at which cancer is diagnosed.
Go get screened today. Spread the awareness during this Mouth Cancer Awareness month.